Next you will find out:
- In what cases it is better to treat wisdom teeth (eights) after all, rather than rush to remove them;
- Why do we need wisdom teeth at all, and how can they benefit you in the future;
- Is it worth treating the eighth tooth if it is badly damaged by caries, and what important nuances should be taken into account;
- In what situations it is necessary to remove the wisdom tooth, and as soon as possible;
- What could be the further fate of the eight in the development of complications of caries, in particular, with pulpitis and periodontitis;
- And, finally, what is the average cost of treatment and removal of a wisdom tooth in a state clinic and in private dentistry ...
The wisdom teeth (the eighth) sooner or later erupt in the majority of people, and not everyone has problems with them. Often, the eights normally leave the gums, without forming a gingival hood, and then regularly perform their chewing function without any signs of carious lesion.
However, this is not always the case - it’s not for nothing that wisdom teeth are considered the most problematic. The most common situation is the difficulty of eruption of the wisdom tooth, followed by its destruction due to caries, and the rating closes its incorrect placement in the jaw, causing injury to the cheek or gum.
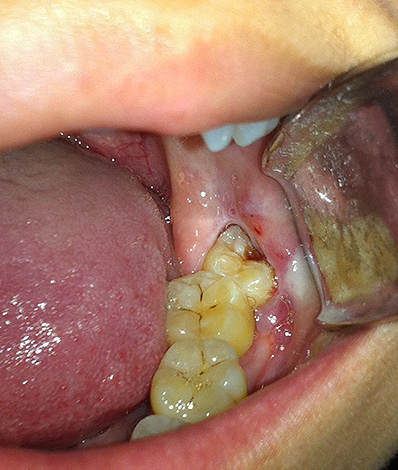
Below the photo shows a polyurethane wisdom tooth (that is only partially cut through):
In a person suffering from pain, in such situations, a quite reasonable question arises: is it really necessary to treat these problematic wisdom teeth, or, perhaps, it is better to remove them immediately from a dentist-surgeon in order not to suffer anymore?
In what cases it is necessary to remove wisdom teeth, and in what situations it makes sense to treat them, as well as some problems that may arise at the same time — we will go on and talk about all this in more detail ...
It is interesting
Wisdom teeth are still a kind of mystery of nature. To date, research continues to dentists associated with the study of the characteristics of the eighth teeth: the unusualness of their structure, position in the jaw, teething, treatment, removal, etc.
Wisdom teeth do not have a fixed number of channels and roots, they may not “break through” the gums throughout a person’s life, they may grow unevenly and create serious orthodontic problems, leading to a violation of bite, may lie horizontally in a bone or even “upside down” ". But often, a wisdom tooth can freely and without any obstacles come into being, without causing any inconvenience to a person and performing a useful (chewing) function.
Why do we need wisdom teeth at all, and when can they come in handy?
There is an opinion that wisdom teeth are an example of atavism - they came to us from distant ancestors who ate roughage, which, if prepared, then without long-term heat treatment. To chew it effectively, a large chewing surface was required — large and strong molars, including wisdom teeth.
Compared with the dental rows of our ancestors, the dental arch of a modern person has become shorter by an average of 10-12 mm - accordingly, there is less space for eights. The food consumed by human civilization has become softer and more digestible, and, in fact, the need for wisdom teeth, in terms of their functionality, has disappeared.
However, wisdom teeth can be very useful in the lives of most people if two basic conditions are met:
- They have a pair - that is, the upper and lower eighth teeth on one (or both) sides of the jaw are a pair of antagonists;
- They are not severely damaged by caries and have no mobility (for example, due to periodontitis) - that is, they can be used in the future as a support for an orthopedic construction (single crown, bridged prosthesis, as a removable denture etc.).
In the first case, everything is more or less clear: why it is necessary to remove a wisdom tooth, if it functionally meets all the requirements for the normal chewing of food. Naturally, in this respect he does not occupy such leading positions as 6 and 7 molars, but he contributes his regular and full contribution.
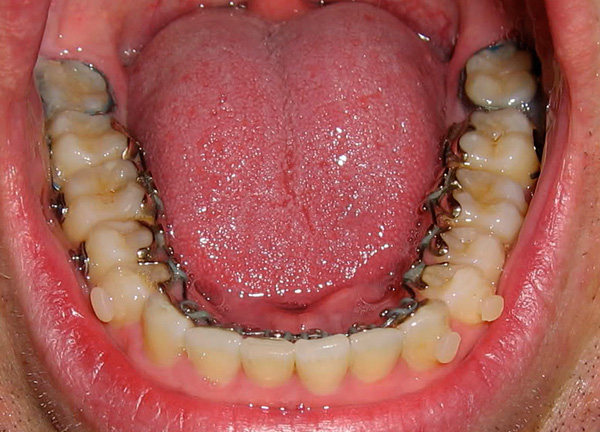
With regard to the wisdom tooth, as hopes for perspective prosthetics in the elderly, one can say the following: if you lose a large number of teeth in the upper or lower jaw in certain clinical situations, it is the eight that can be an excellent support for the future prosthesis in the broad sense of the word.
An example of using a preserved wisdom tooth as a support for a partial denture is shown in the photo below:
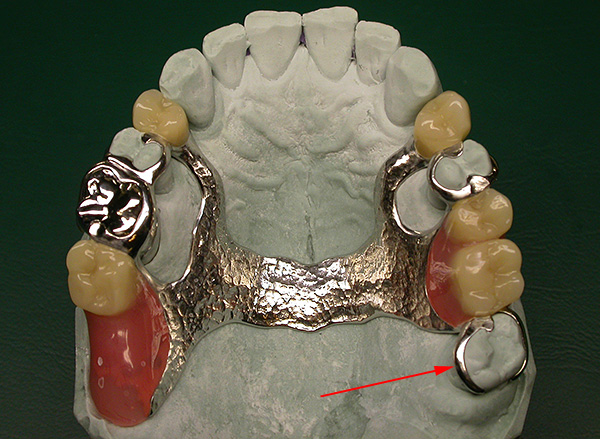
From the practice of the dentist
Often, a wise tooth becomes the last hope for a bridge - then why, one wonders, without a compelling need to pull out a wisdom tooth, which, if it loses the end teeth important for prosthetics (6 and 7), can be a reliable support for the bridge coming from the five (premolar).
Even in the case of some destruction, the wisdom tooth can become a support under the crown, and that, in turn, will serve as a supporting element for fixing a partial denture (byugelny, laminar, butterfly-prosthesis, etc.).
So, as you can see, wisdom teeth should be protected and if there are opportunities to heal, and only be removed as a last resort, when there are appropriate indications for this. However, with regard to indications for the removal of eights, there are some subtleties - let's consider them further. And let's start, perhaps, with the question of the need to remove wisdom teeth with their carious lesions ...
Is it worth treating a wisdom tooth if it is affected by caries, or is it better to remove it immediately?
As a rule, independently finding yourself caries on the teeth,patients come to dentists therapists who are directly involved in dental treatment (that is, they are conducting therapy).
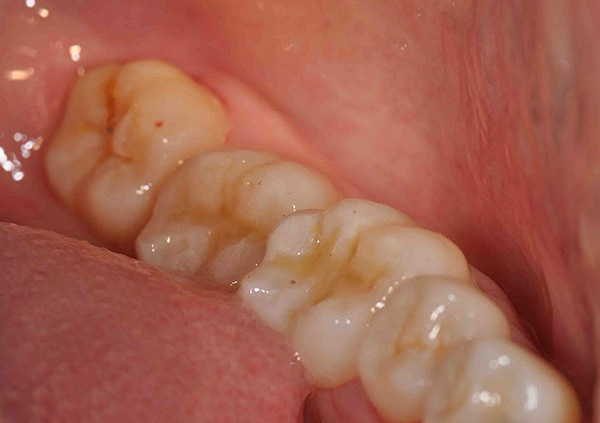
Let's see how the dentist therapist decides whether the eighth tooth can be treated with caries, or we should think about removing it, referring it to the dental surgeon.
Example # 1: there was no problem with the eruption of a wisdom tooth, and he fell into place without injury to the oral mucosa, however, on its surface (chewing, contact, or others), over time, foci of caries appeared. In this case, it is not necessary to remove the wisdom tooth, but it is advisable to treat it, and as early as possible so that the carious process does not go deep into the pulp chamber (to the “nerve”).
However, even if the tooth pulp is affected and it is no longer a matter of caries, but of pulpitis - even in this case, the wisdom tooth does not need to be hurried to be removed, it is only necessary to treat the canals and install a filling. The tooth will be "dead", but it can serve for a very, very long time.
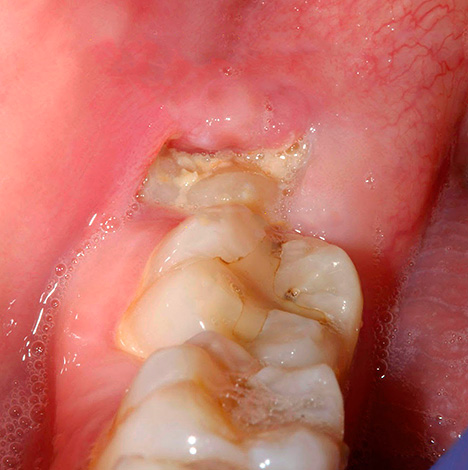
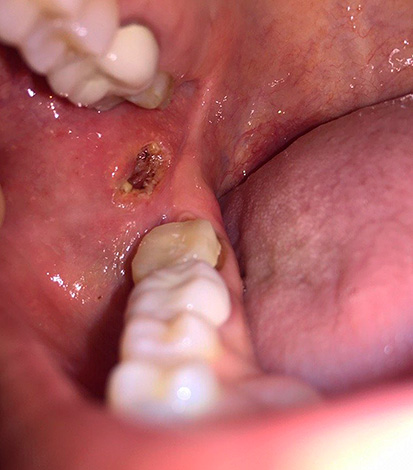
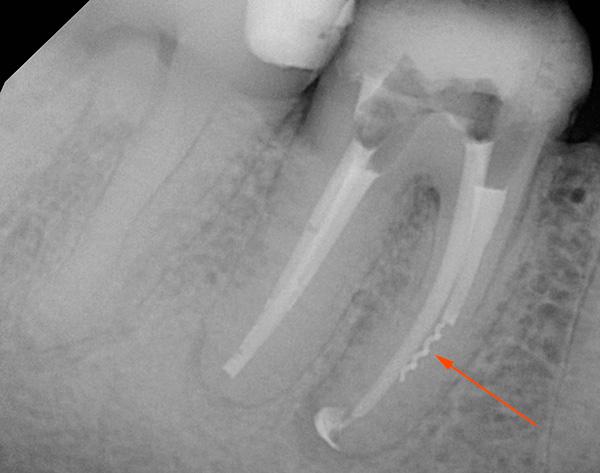
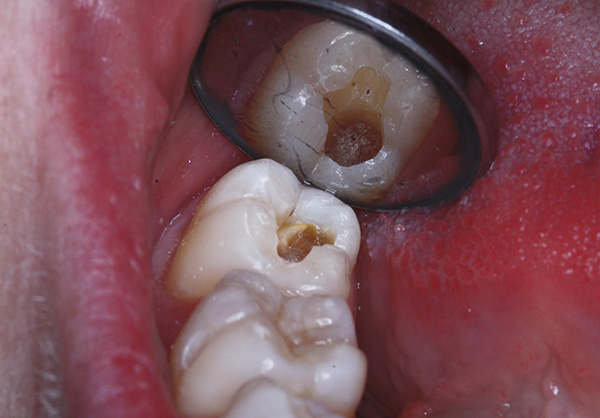
The picture below shows an example of significant decay of the wisdom tooth:
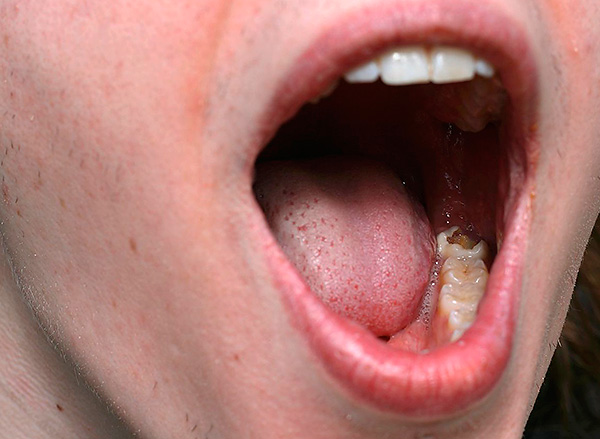
Now we will consider situations when it is not always advisable to treat a wisdom tooth with caries, and sometimes it is better to remove it as soon as possible.
Example number 2: significant destruction of the wisdom tooth with its incomplete eruption. In other words, only a few hillocks of the wisdom tooth appeared above the gum, and the rest of it is under the gum, but serious carious destruction is already observed.
Wait, when the wisdom tooth is all on the surface for its full treatment, or, especially, to endure recurrent pain, temperature and swelling when it is difficult to penetrate - there is no sense, this is a vicious practice. Of course, this does not apply to superficial caries, or even medium with relative comfort (no pericoronitis symptoms). However, monitoring the situation is also important here so as not to miss the destruction of the tooth to such an extent that it will have to be removed anyway, but already against the background of serious complications (periostitis, osteomyelitis, abscess, phlegmon).
Example No. 3: incorrect position of the wisdom tooth that has erupted in the jaw in the presence of significant carious destruction (including the situation that impedes the hygiene of the 7th tooth). When a wisdom tooth has a significant deviation from the normal position in the jaw,it can be difficult to provide adequate hygiene, as a result of which caries progresses rather quickly, and the seven may also be involved in the process. In addition, there is often a violation of the bite in general.
Be that as it may, in practice each situation is individual, and the doctor decides whether to treat a wisdom tooth or remove it, taking into account the specifics of a particular clinical case.
It is interesting
Even if you signed up for a wisdom tooth extraction dentist, it is not a fact that he will remove it for you. The fact is that dentists-surgeons are engaged not only in the extraction of teeth, as people commonly think, but also in their rescue by performing tooth-saving operations (and if they are removed, then only with clear indications).
If we are not talking about any indifferent doctor in a seedy clinic, then it is the dentist-surgeon who will help you to establish exactly whether you need to remove a wisdom tooth right now or you can try to save it.
A few words about the treatment of caries of the eighth teeth
So, with the defeat of a normally erupted and properly functioning wisdom tooth by caries, there is no need to hurry to remove such a tooth, it is enough to carry out its full treatment.
Almost always, in such cases, the classical preparation of the carious cavity using a drill is used as a preservation technique.
On a note
Modern dental units provide the frequency of rotation of boron at the level of 80-100 thousand revolutions per minute. At such a speed, the contact of boron with hard tooth tissues in the absence of forced cooling would lead to strong heating, therefore, air-water cooling of the tip is used.

Let's look at a number of popular issues related to the treatment of wisdom teeth affected by caries.
Patient question number 1: is it painful to treat caries on the wisdom tooth?
At the stage of superficial or even average caries, a wisdom tooth can now be treated absolutely without pain, even without the use of anesthesia. The fact is that during the work of a handpiece that meets the requirements of dentistry of the 21st century, there is practically no vibration (as it happened before) and overheating of the tooth, which almost always excludes the formation of pain. However, in hypersensitive people, as well as in the treatment of deep caries, it is preferable to conduct anesthesia.
Patient Question # 2: Last time when treating caries of the lower wisdom tooth, I froze the floor of my face for 6 hours, is there a softer alternative?
The question is really relevant. Many dentists work according to the old principle: knowing that the classic infiltration “near the lower eighth tooth” will not be very effective, they immediately make conduction (torus or mandibular) anesthesia, which determines the duration of “freezing” up to 6-8 hours. That is, the patient does not feel his cheek, lip, tongue, etc. for quite a long time.
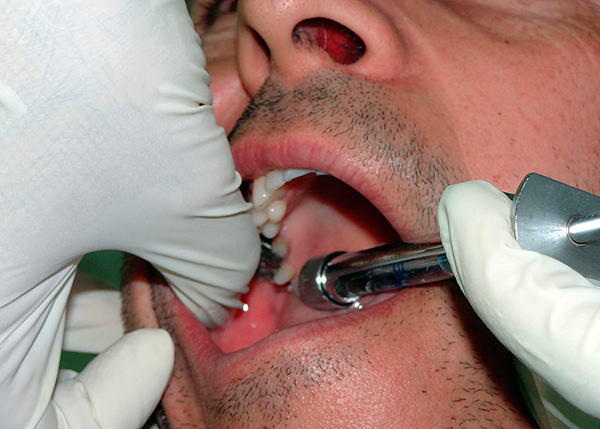
Modern alternatives are the types of infiltration anesthesia - intraralgamental (intra-cohesive) and intraseptal (intra-septal). The amount of anesthetic injected with these techniques is minimal, and if they are precisely observed, the effect is very high: within 40-60 minutes, the caries of the wisdom tooth can be cured absolutely painlessly, and at the same time, half of the face will not freeze. However, not all doctors are perfectly fluent in this anesthesia technique.
The upper wisdom teeth, in contrast to the lower ones, are perfectly anaesthetized by the classical infiltration method: by bringing the solution to the root, which excludes the phenomenon of long-term loss of sensitivity of facial areas.By the way, to remove the upper wisdom teeth in most cases is also much easier than the lower ones.
Patient No. 3 question: can two wisdom teeth be cured in one visit?
Old school doctors may start scaring that the caries of the two lower teeth at the same time are dangerous to treat because of the same conductor anesthesia on the “half of the face”, which will cause a loss of sensation of the tongue, may lead to the development of suffocation, etc. In spite of the fact that it is a myth, it is preferable to treat the two lower teeth with an intraligamentary or intraseptal anesthesia (or without anesthesia, if possible). Those who are ready to sit in a chair for more than 2 hours should bear in mind that a professional dentist can cure all 4 wisdom teeth in one visit, so two eights are not the limit.
It is interesting
When treating teeth, patients often make the remark that the doctor over-drills a tooth - they say, it is too long and very hard to grind off a drill. Young doctors such complaints really baffled.
The fact is that you can “grind off” a significant tooth piece very quickly, in just a couple of minutes. But precisely because of the desire to achieve high quality cleaning of carious tissues, the preparation process is not so quick.Sometimes this painstaking work has to be spent from 5 to 30 minutes - in order to minimally affect healthy tissues and clean out necrotic as much as possible.
In some cases, wisdom teeth is desirable to still remove
Now consider the situation where a dentist has the right to recommend to remove a wisdom tooth, even without signs of carious destruction.
The main indications for the removal of wisdom teeth:
- A impacted or polyurethinized tooth (i.e., in the event of problems, when the tooth cannot erupt, or partially erupted). Naturally, each case is individual. A impacted wisdom tooth can stay under the gum for a long time and not cause concern, as well as a polyurethinized tooth can be the result of a more or less normal partial eruption of the crown part. If there are no symptoms of obstructed eruption, then there is nothing to worry about, however, with severe symptoms (swelling, severe pain, high fever, festering from the gums near the tooth), the doctor may decide in favor of removal - and almost always will be right;
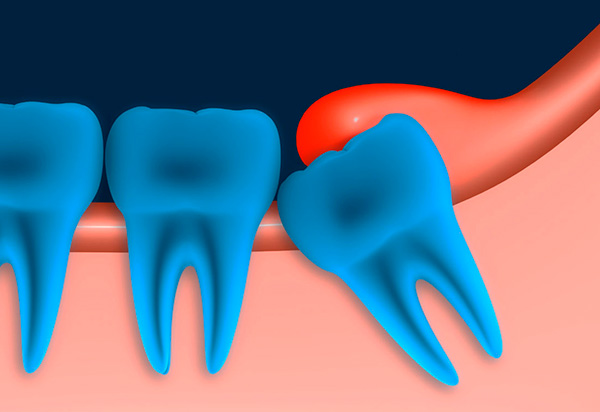
- Dystopian wisdom tooth - that is, when it occupied the wrong position in the jaw.It is not always necessary to remove such teeth. If a figure-eight that is cut in the direction injures the mucous membrane of the cheek or tongue, then it is necessary to remove it (a chronic injury can lead to the development of malignant tumors). In other cases, options are possible, depending on the situation in the oral cavity as a whole;
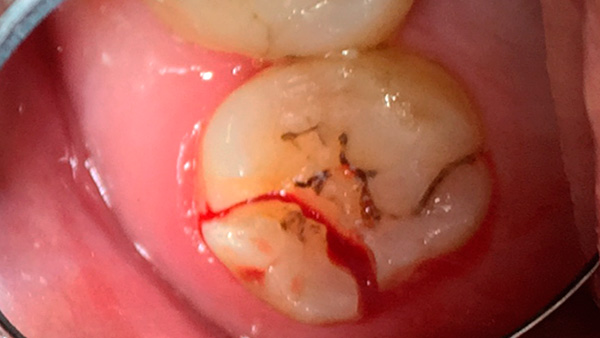
- Significant mechanical destruction of the crown of the wisdom tooth (for example, cleavage extending far under the gum), when its restoration with the help of a tab and an artificial crown is not possible;
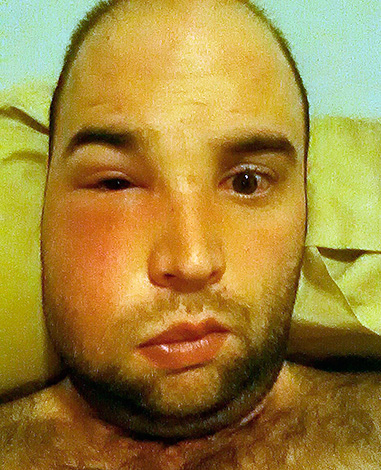
- The active stage of serious purulent complications in the form of exacerbation of periodontitis, periostitis, osteomyelitis, abscess, phlegmon, etc. (including can be observed after the treatment of canals in the wisdom tooth). With regard to the lower wisdom teeth, delay in such a situation is like death, so it is imperative to remove it. The lower jaw is massive, the spaces in it are wide, the risks of leaving the infection deep into them are high, even fatal. If we talk about the upper eights, in exceptional cases, you can take up the treatment of exacerbation of periodontitis or incipient periostitis, but in this case it is necessary to take into account all possible risks;
- The impossibility of conservative treatment for one reason or another. It happens that a dentist, taking up a wisdom tooth treatment, may face the fact that he cannot continue this treatment - for example, complications arise (a piece of instrument in the canal with no equipment for its extraction, root perforation, over-expansion of the canal), or a doctor cannot find and (or) along the entire length process and fill the channels with high quality. In some such cases, a more qualified, experienced dentist with the necessary equipment can help, but such experiments always cost a pretty penny, and not every patient can afford it;
- Orthodontic treatment. Today, the orthodontist’s tactics before removing the same bracket systems to remove wisdom teeth, especially those who, being impassable, run into the adjacent sevens, as if pushing the entire dental row, have become popular. Studies have shown that this is justified, since the success of correcting bite while maintaining interfering wisdom teeth is questionable. However, it is not always necessary to delete eights when installing braces.
Do I need to remove a wisdom tooth in violation of hygiene 7 tooth?
It has already been noted above that in such cases wisdom teeth are sometimes actually removed. However, at the moment this issue is considered controversial: a number of experts believe that it is worth deleting, as in practice, the walls of the 7th tooth destroyed by caries, adjacent to the wisdom tooth, are often found. Others believe that the seventh tooth can always be cured if it is suddenly sore, but at the same time, a figure eight, even with insufficient hygiene, can serve a person for many years before it makes itself felt.
Is it necessary to treat the complications of caries in prospective wisdom teeth?
If a tooth is not treated in time at the stage of carious destruction, then further complications of caries develop - pulpitis, and then periodontitis. Will the treatment of the channels of the wisdom tooth be promising in such cases?
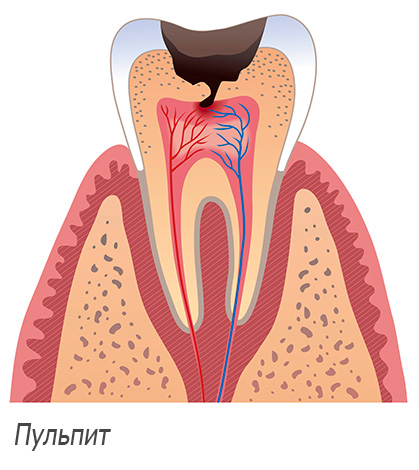
Let's start, perhaps, with pulpitis, as one of the most common diagnosis at a dentist’s appointment.
On a note
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the neurovascular bundle (“nerve”) inside a tooth, when this tissue, in spite of the inflammatory process that has begun, is still more or less, but alive.
If it was not about the wisdom tooth, then any dentist-therapist would say with certainty that there is no need to remove a tooth, it is enough to treat the canals. However, a wisdom tooth, unlike the others, has an unpredictable number of channels, its roots are often bent, and access for comfortable and high-quality treatment is most often difficult (especially when treating upper eights). Under the conditions of an ordinary state polyclinic, it is not always possible to properly treat such a tooth, and further complications may arise.
At the same time, high-quality endodontic treatment is possible in dental clinics of the business class with pulpitis of almost any, even the most unusual in structure of the wisdom tooth - with monitoring of the processes in the image, using a dental microscope, ultrasound equipment, apex and other auxiliary devices. However, the price of this service will be considerable.
On a note
There is an opinion that there are no "impassable" canals of the teeth - but there is a lack of good specialists and the necessary equipment. That is, if the doctor hints at the removal of the eight and says that with the pulpitis, the wisdom tooth cannot be cured,since it has curved or narrow channels, it can only be stated here that either the clinic does not have the appropriate equipment or the doctor is not experienced enough.
If you have a strong desire to save the wisdom tooth from removal, it is best to consult 2-3 doctors. If 2-3 doctors tell you to remove a wisdom tooth, and the sooner the better, then this should be done.
When the inflammatory process in the pulp chamber goes far, the pulp dies off, and we are already talking about the diagnosis of periodontitis. In this case, the doctor considers the feasibility of preserving the tooth in terms of risk to the patient's health - depending on the form and stage of the process, it is possible to begin treatment of the canals for acute forms and for chronic fibrous periodontitis.
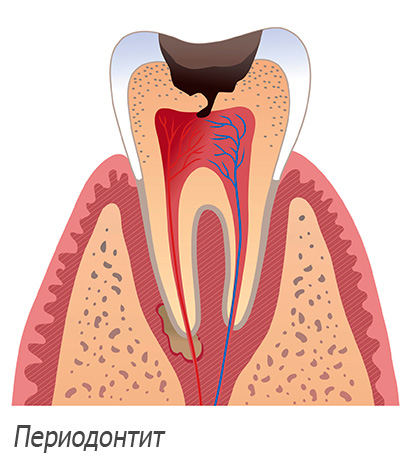
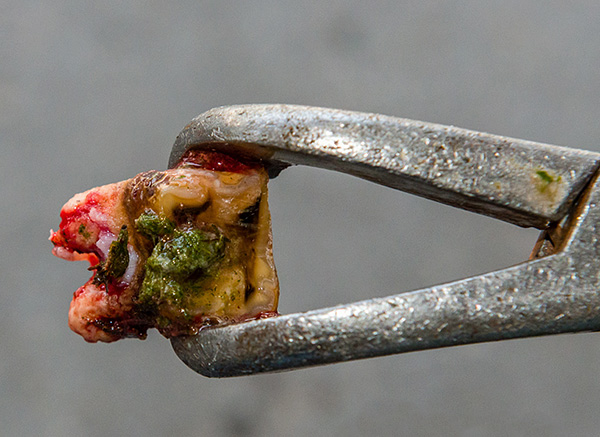
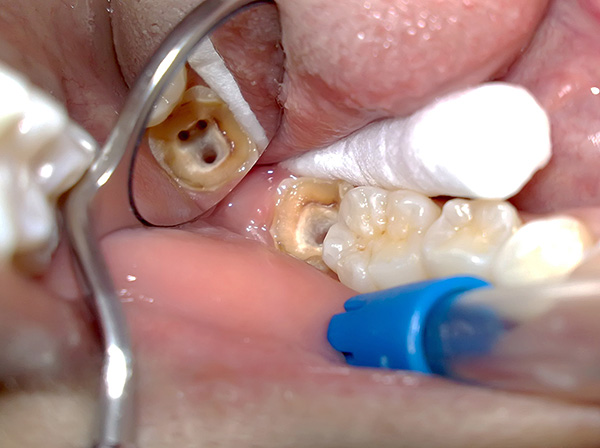
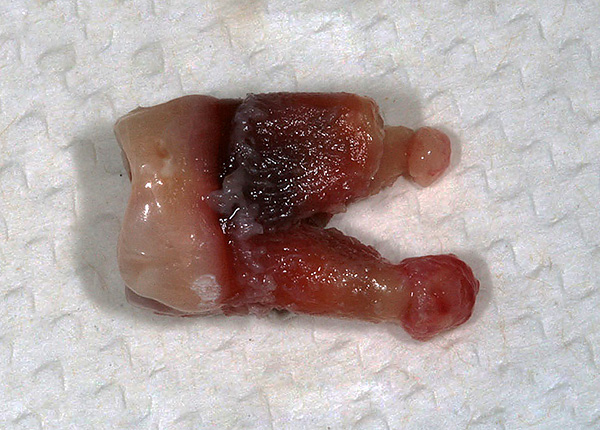
If we are talking about granulomas, cystogranulomas, cysts, then most often the wisdom tooth is removed “away from sin”, although sometimes according to the testimony can be selected and tooth-saving techniques. Here to decide and take responsibility for the doctor.
The photo below shows the extracted tooth with cysts on the roots:
On a note
Periodontitis periodontitis - strife.In acute forms (especially in the serous stage), as well as in chronic fibrous and granulating periodontitis, the ability to preserve the wisdom tooth is significantly higher than with granulomatous periodontitis. In general, the words “granuloma”, “cystogranuloma” and “cyst” should warn you that the treatment may not be entirely successful, or the doctor will immediately suggest that you remove a wisdom tooth, and this will almost always be a justified decision.
How much can the treatment and removal of wisdom teeth
Now, when you have a general idea of when it is possible to treat, and in which cases it is preferable to remove wisdom teeth, let's see how much the corresponding procedures can cost and whether it is possible to somehow save money.
So, if you carry out treatment in a public institution at the place of residence (hospital, clinic), it is almost always possible to save a lot, but to get far from the highest quality service. The removal of a wisdom tooth is an extreme measure, and in the same hospital it can be removed for free under the so-called “Krikain” (in the language of dental surgeons, this means that anesthesia does not work, and the patient literally screams in pain).At the same time, there is also a high risk that the roots of a tooth that are not completely removed remain in the hole - the doctor has too little time for one patient to pay due attention to all the important points.

As for the removal of the wisdom tooth in private dentistry - it will cost significantly more than in the state clinic. The upper wisdom teeth in 70-80% of cases fall under the statistics of "light" teeth, and after analyzing the snapshot, the issue of price is solved within the limits of 2,000 rubles for the removal of one eight.
Lower wisdom teeth, especially the impacted and polyurethinized ones, can be removed at a high price: from 3 thousand rubles to 8-10 thousand in one procedure. In some cases, anesthesia and hospital stay are included in this price.
Treatment of caries on the teeth of wisdom can come at a price of 2-3 thousand to 7-8 thousand rubles for one tooth. The price for the treatment of the canals of the wisdom tooth largely depends on the number of these canals: if there is one canal, then for its endodontic treatment usually take about 1000 rubles. With the increase in the number of channels (and there may be 4-5), the cost of endodontic procedures is also increasing proportionally.
It should be borne in mindwhat is considered separately (plus) anesthesia, the use of cofferdam, drugs (drugs) for drug and anti-inflammatory canal treatment, temporary and permanent fillings, etc. As a result, the complete treatment of a wisdom tooth with pulpitis can cost 5–20 thousand rubles, and the treatment of periodontitis is even higher.
In conclusion, it should be noted that for many patients wisdom teeth are as important as any other tooth, and they are extremely reluctant to part with them. Meanwhile, there are many such patients who, in the event of problems, are not willing to spend time and money on preserving their wisdom teeth, and at the first opportunity remove the eights without regret. Anyway, the dentist cannot make a decision for you: he can only put accents, weighing all the pros and cons, but the patient will always have the last word.
Be healthy!
Useful video: when the wisdom tooth is desirable to remove
An example of removing a polyurethinized wisdom tooth with preliminary cutting it into pieces ...

They all say that it does not hurt, etc. Just come. For 10 years, I have never met a doctor who would not have treated painfully. Alas, ah ... Our medicine leaves much to be desired. No pain - if only under general anesthesia.
I have a doctor who treats without pain.
Yesterday the tooth was removed. Removal with local anesthesia - 12 thousand, and this is not the most expensive and with a 10% discount. And in the article some ridiculous prices are indicated, from 3 to 8 thousand. During the removal, all the buzzing.It became painful only when the anesthesia began to withdraw, and that is tolerable.
Guys, I'm with you. Pain in the tooth after the canal filling. Dead tooth for 15 years - and then managed to naparachit.
Hello! Tell me, please - on my right side I regularly have a headache on the exit points of the trigeminal nerve - above the eye, the maxillary sinus, teeth. Neurologist and ENT problems do not see, they say that a possible reason is a wisdom tooth. Both teeth on this side erupted, the upper one came out completely, but it began to unfold along the axis, while in the lower 30% it was still under the hood. Can wisdom teeth cause such headaches? And which tooth is more likely to blame, upper or lower? The pain is most often felt in the upper row, with teeth whining from 6 to 8.
The implantologist also said that wisdom teeth should be removed before prosthetics - is this statement true? (It is necessary to replace the lower 6, both were removed because of the cysts under them).
Hello! In some cases, wisdom teeth can actually cause pain in adjacent teeth, headaches, etc.In the presence of significant pathologies, they really should be deleted. What kind of tooth is to blame (upper or lower): it cannot be determined in absentia. X-ray images can be used to try to determine the originator of the problem, but even in this case it is not always easy to do.
If you are going to have prosthetics, and the implantologist recommends removing wisdom teeth with the pathologies described by you, then you should listen to the opinion of the doctor. As a last resort, you can get advice from another 1-2 specialists and get their opinions on this. And then make the final decision.
Yesterday I removed the lower wisdom tooth for 1,200 rubles, while I warned the dentist that I was registered with an infectious disease specialist.
10 years ago I had an 8th tooth removed in the lower jaw and everything went fine (the doctor split it and removed it). A year ago, I decided to remove it from the other side: the tooth was sawn (another doctor removed), and then pulled out piece by piece. But after the removal, something terrible happened. My face has drastically lost weight, ear pressure has begun, tongue twisting, dizziness, nausea, a feeling that something has broken and dispersed under the gum, the joints began to go out of their normal position.I complained about a very bad state of health, but I was told that the dentist had nothing to do with it.
I began to look for a connection between the ear and the lower jaw and it turned out that it was Meckel's cartilage. I talked with an independent expert and he told me that there was a film. It turns out that when I was removed, the doctor damaged the plenum (reduced Mekkelev cartilage). The attending physician burns: "Mikkelev cartilage is an intrauterine organ that turns into bone." And in the encyclopedia of Brockhaus and Efron it is written: "With the development of the bone skeleton, the m. Cartilage is pushed aside by the mandibular bones, which develop near it, and is reduced, giving, however, the beginning to some auditory bones (hammer).
Meckel's cartilage was discovered in 1820. Less than two hundred years have passed. We have new technologies: CT, MRI and other types of research. Then why is this happening ?! Before the removal, I did not complain about my health.
If the wisdom tooth does not bother you, do not touch it !. There are a lot of legends about him - this is from ignorance of the structure of the lower jaw. For many centuries they could not explain what was happening. Therefore, people called the 8th wisdom tooth. Only in 1820, the German biologist I. Mekkel was able to solve this riddle.I would never know the truth if what had happened didn’t happen to me.
Hello! Consilium on your problem is desirable, since I alone with my opinion can hardly insist on any truth. Personally, I have not met in 11 years of working with a phenomenon like yours, although I have removed more than one hundred wisdom teeth. I'm pretty sure that your case is 1 for several thousand (and maybe less). There are a lot of mysteries here, and it creates the feeling that you need to understand and once again understand this complication. It may even be that you have a problem for an entire scientific work that draws on a doctoral thesis. I say this without any irony, but only for reasons of the alleged rarity of such a complication. I do not condone your doctor, but I understand one thing: if I have not heard anything about such a phenomenon, this does not mean that it cannot happen. I am sure that you should contact a specialist who has access to a consultation of experts of a different profile: professor of anatomy, pathology, maxillofacial surgeon, radiologist.
Meckel's cartilage is a cartilaginous arch that covers the oral cavity from ear to ear, jointed to the hyoid arch and complex joints attached to the base of the skull,and also serves as a suspension for the lower jaw of a person. In an adult, cartilage is reduced (modified) and transformed into a film. Damage which is very dangerous!
Thanks for the answer. This tooth was removed by the doctor of the district hospital. When I realized that something bad had happened, then I turned to regional dentistry with complaints of feeling unwell. I was taken a picture that I flatly refused to give. And I had to contact Roszdravravnadzor. And only three months later I received a snapshot. I do not know if this is a snapshot (3D disk, computed tomography). I have doubts. And you speak about a consultation.
I want to add. Before removal I was given an injection, everything was numb. When the doctor sawed me the 8th tooth in the lower jaw, I felt that I was sawing something, I would call it as a “bundle”. The doctor made a second shot, but it did not help. I remember this terrible feeling. At home for five hours there was numbness after two injections.
Of course, I took pictures in paid hospitals. I can say: the dentists see the damage, but no one wants to give a conclusion. Talking do not even burn with desire.And you speak a consultation! Here is a mystery!
I don’t understand why some doctors know about Meckel cartilage, and others don’t. After all, the structure of the lower jaw is studied by all dentists. Some are surprised. Or maybe this surprise is due to the fact from where I learned about this cartilage? Why did I need to deeply study the structure, to seek an answer. There is a reason for this. And this reason - the deterioration of my health. Although a lot of time has passed.
Meckel's cartilage is in every person. It is impossible to deny. The location of the tooth may be different - yes. The fact that I have a complex 8 tooth in the lower jaw, the doctor told me long before the removal, when this tooth I only grew. I was shot "hood" (cut the gum) over the tooth. But I could not imagine what awaits me. That is, I can say that I do not have such teeth alone, and this is not news for doctors. Doctors met these teeth, and I'm not the first. And an ordinary person does not know about Meckel's cartilage, and why should they know? I think that is how doctors argue. This is their little secret! Who will study the structure, starting with fetal development. An ordinary person will not. Know less - sleep better. But I will not wish this damage to the enemy.
Hello.Tell me, please, if a wisdom tooth climbs already with a very large caries and at an angle of 40 degrees, and the tooth process is very large (half of the tooth in the gum, and there is a sharp piece of tooth sticking to the cheek) - what should I do
Hello, a wisdom tooth with a slope and caries affected is at least a chronic infection, which in most cases cannot (reliably) reliably cure therapeutically. Leaving such teeth is usually not recommended because they eventually lead to inflammation. Therefore, in your situation it is necessary, without waiting for the appearance of pain and inflammation, to consult with the dentist-surgeon - most likely, you will have to routinely remove the tooth.
Tell me, where in Moscow are dentists who will not be about a normally grown eight with a hole for a third of the volume of the head categorically insist on distance?