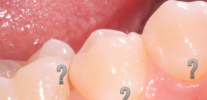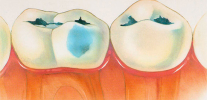
From the point of view of the causes and development of the pathological process, caries under the gum is no different from caries on the eye-visible surfaces of the teeth - contact, cheek, palatine, and others. Its main feature lies in the unusual arrangement and associated difficulties in the timely detection and treatment of this form of the disease.
At the stage of stains and superficial caries, when such a pathology does not yet cause severe pain, it is impossible to detect damage to the teeth covered by the upper part of the periodontal tissues with a simple examination of the oral cavity. For this reason, the treatment of a diseased tooth with caries located under the gum usually has to be taken at the stage of progressive pulpitis, which produces a pathological process with pain of different severity.
Today, subgingival caries is successfully diagnosed and treated in the early stages of development, but this requires a high consciousness of the patient himself,who agrees to visit the dentist only for examinations and detection of the disease at those stages when it does not cause concern. Much in the diagnosis of caries under the gum depends on the doctor, who must be able to properly assess the cariogenic situation in the mouth and suspect the presence of the disease with non-standard localization, even without obvious signs of its presence.
Localization of caries under the gum
Caries when localized under the gum may be located, generally speaking, on either side of the tooth. However, practice shows that more often it develops on the proximal surfaces, that is, in the interdental area (interdental caries, which began initially over the gum, tend to quickly go under the soft tissues, which can lead to root decay).
The photo below shows the extracted tooth with caries-affected area of the root:
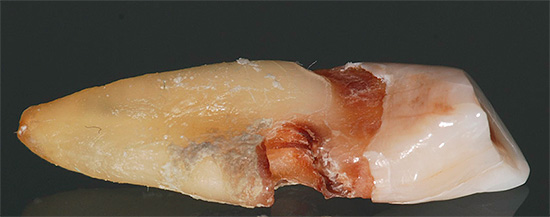
The entire cavity formed as a result of caries was located below the edge of the gums, and therefore the tooth seemed to look healthy, but at the moment, after some time, we can observe a neglected carious process that led to such a radical decision of the dentist.
In many cases, during the development of caries under the gum, the pathological process does not capture the visible areas of enamel even in the later stages of development., and as a result, the disease develops safely to the stage at which pulp is affected.
On a note
Caries located under the gum should not be confused with a disease which some patients call “caries on the gums”. The second nosology is a typical cervical caries, developing exactly along the periodontal edge. At the same time, of course, he does not go to the gum itself, since it can only affect the tissues of the tooth. Caries developing under the gum sometimes can spread to areas above the periodontal edge, but during its treatment and cleaning of carious cavities can be clearly seen when caries develops on the neck of the tooth, and when under the gum with further capture of the surrounding areas of enamel.
A carious cavity under the gum is a kind of “food collection” that provokes the gum to regular irritation with the development of traumatic or infectious inflammation of the type of gingivitis or even periodontitis.
Hazards and consequences of caries under the gum
Like other forms of caries, caries, localized under the gum, may have minimal signs on the outside of the enamel, but at the same time penetrate deep into the internal tissues, which leads to imperceptible tooth decay. Therefore, in such cases pulpitis develops quite often and depulpation (removal of nerves) is required.
Much less often, the unhealed caries that develops under the gum can so seriously affect the root that the tooth must be removed.
Besides, tooth decay faster leads to inflammation of the pulp than caries that develops from the surfaces of the tooth above the gum. The distance from the root wall to the pulp is small, and even a very large lesion is enough for the soft tissues of the tooth to become involved (they are called “nerves” by the people).
In addition, it is under the gum caries has more opportunities to develop into periodontitis. As it develops and the enamel is destroyed, the space between the tooth and the gum increases, more and more food accumulates and rots in it, which leads to rapid irritation and inflammation of the gums. Although in most cases, already at the stage of pulpitis, the pain in the tooth becomes so acute that, prior to periodontal inflammation, the patient already see a doctor and receives appropriate treatment.
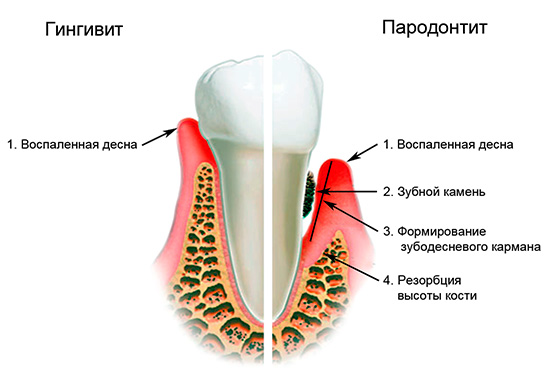
Causes of pathology
Caries under the gum can develop for many reasons. The main one is gum disease, in which pockets are formed between the surface of the tooth and the gum adjacent to the neck of the tooth. Food pockets and bacteria that produce cariogenic acids easily penetrate into such pockets. As a result, it creates a very favorable environment for the development of caries.
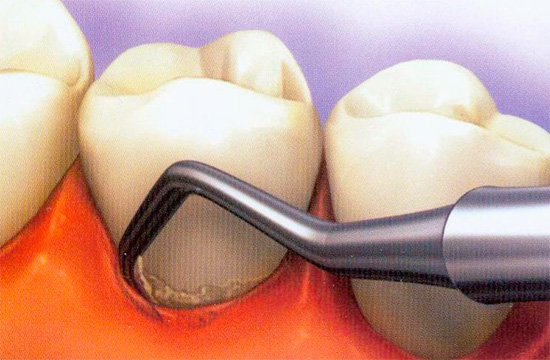
In addition, the disease may develop for the following reasons:
- improper installation of crowns, in which the gum is lowered or mechanically retracted (peeled off) from the tooth;
- lack of good oral hygiene;
- some diseases, due to which saliva production decreases, or its composition and, as a result, bactericidal activity changes.
And, of course, as with other types of caries, the destructive process under the gums can be triggered by a diet with an abundance of carbohydrates (mainly sugar and flour) and hereditary factors - susceptibility of teeth to caries, thinness of enamel and others.
Symptomatology and diagnosis of caries, localized under the gum
Caries, located under the gum, almost does not pretend to be those symptoms that are characteristic of cases of localization of pathology in the open areas of enamel. Since the affected areas of the external walls of the tooth are protected by periodontal here, cold and hot products almost do not fall on them, and therefore even deep caries may not cause pain here.
Only in cases when the pocket between the gum and the tooth is filled for a long time with the remnants of rotting food, can the patient be slightly disturbed by the tooth itself, and the gum that is traumatized or irritated by the food remains. With a certain experience, the patient will be able to distinguish between these types of painful sensations, and the doctor according to his words will carry out the correct diagnostic methods.
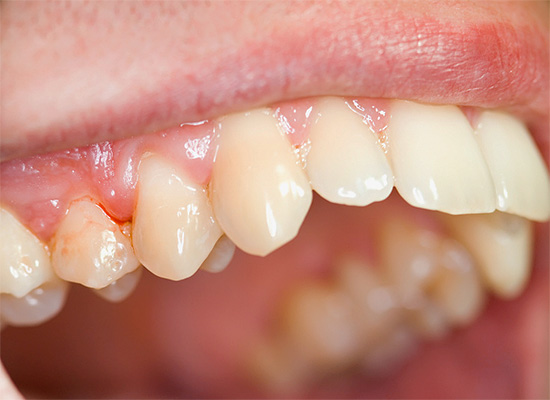
Thus, it is possible to suspect the development of caries under the gum only with the appearance of pain in the tooth or soft tissues adjacent to it, and before that the lesion can be detected only by chance during special diagnostics of neighboring teeth using x-rays, transillumination or laser devices.
Important!
Specially prescribing x-ray apparently healthy teeth without suspicion of caries, the doctor will not.Therefore, it is very important to pay attention in time to the first signs of pain in the teeth and arrive at the examination as soon as possible. With such self-discipline, even the caries hidden under the gum can be diagnosed at a stage when, to eliminate it, reaming and filling of the tooth is not required.
Specific treatment of caries under the gum
In principle, the treatment of caries under the gum does not differ from the tactics of caries in other areas of the tooth.
If the enamel is damaged only partially and the pathological process has not spread to the dentinal layer, it is possible to clean the affected area with special polishers and to complete the course from the procedures for mineralization. This allows you to restore the enamel.
If a part of the dentin is covered by the disease, the doctor removes the part of the incomplete enamel covering it, cleans the carious cavity and installs a filling. When the pathological process covers the soft internal tissues of the tooth, it is necessary to depulpate the tooth.
Subgingival carious processes almost always require gum correction (excision, coagulation, etc.) at the beginning of work and further isolation of the working area from blood and saliva.These manipulations, on the one hand, complicate the treatment and take extra time, but give the opportunity to qualitatively cure a tooth with such a problem.
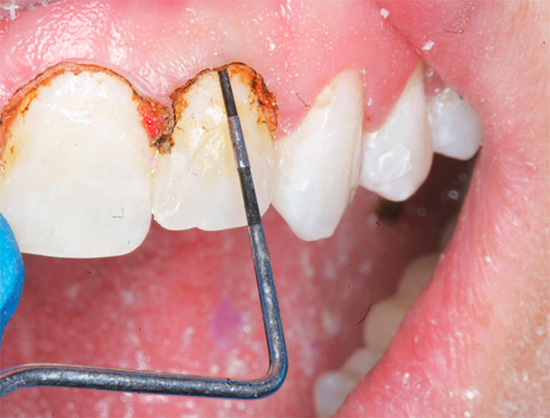
On a note
To create maximum dryness of the surgical field and to control gingival bleeding, dentists often use cofferdam in such cases. This is a piece of rubber (latex), the function of which is to isolate individual teeth from the mouth during treatment.
If it is not possible to use a cofferdam, the dentist is forced to use glass-ionomer cements that are resistant to moisture when used as a filling material, since it is impossible to completely eliminate the ingress of saliva and blood into the work area. However, these materials have low strength compared to composites, high abrasion and poor polishing. These negative properties directly or indirectly affect the quality of the future under-gum filling, but this is better than the one that fell out every other day or immediately from the composite. At least, the JRC can be given a guarantee.
If the clinic uses cofferdam, then even with relatively deep lesions of the tooth root, it is possible to effectively isolate it from saliva and blood, and more aesthetic and versatile composites can be used as a filling material. Although in a number of clinical situations, it is necessary to apply, again, glass-ionomer cements and compomers (fillings that combine the properties of GIC and composites).

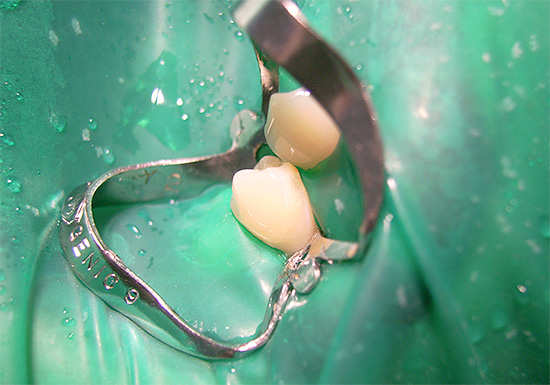
On a note
The use of cofferdam today has not yet become the standard in domestic dentistry, and such a film can be seen mainly in elite and very expensive clinics. However, practice shows that with its use in more complex places it is possible to install the strongest and most durable fillings, and in general, the treatment is more qualitative.
Depending on how far the pathological process has gone, different treatment options for caries are possible:
- With a small lesion, when pulp is not involved in the pathological process, the carious cavity is cleaned with a drill and filled with a filling material.
- If more than 60% of tooth tissues are damaged by caries or if one or several of its walls are significantly damaged, inlays are installed. Sometimes it is only possible to install a tab with a pin.This is done in cases where at least one tooth root and a large part of the crown are affected, from which at least one wall remains after cleaning the carious cavity.
- If carious damage covers the entire crown of the tooth, but its roots remain intact, it is possible to install an artificial crown on a living tooth;
- If one or several roots are affected, as well as most of the crown, the latter is removed, the tooth is depulped, the stump insert and the artificial crown are set.
In some situations, caries developing under the gum may lead to the need to remove a tooth. This happens if the deep parts of the root are covered by the pathological process. Cleaning them is extremely difficult due to the fact that the tool interferes with the alveoli, and even if this can be done, the pin for the tab will have nothing to attach. In these cases, the tooth is removed, and at the request of the patient in his place in the future, install the prosthesis.

It is possible to decide on a particular treatment option only after opening the carious area, cleaning it and determining the amount of tissue damage.
Almost always, caries treatment under the gum is carried out under local anesthesia. Therefore, for the patient, this process is painless and does not cause much discomfort.
Prevention rules
The main opportunity to prevent the development of caries under the gum is to undergo check-ups at the dentist in time. This is a universal measure that will protect those who can boast of healthy and strong teeth, and those with sufficiently susceptible teeth to caries.
It is also important to perform dental treatment and install crowns with a doctor with extensive experience. He will not make mistakes and will not put the crown in such a way that this operation will provoke the development of caries.
For the prevention of caries under the gum, all the rules common to other types of caries are relevant: regular thorough cleaning of the teeth, correction of the diet with restriction of sweet and flour, removal of food debris from the mouth, eating foods with a temperature close to the body temperature. And of course, it is very important to monitor your own feelings and consult a doctor at the first sign of pain in the tooth. This will guarantee timely and successful treatment.
The main causes of tooth decay (including under the gum)
Interesting video: from which periodontitis and its potential danger
Offset of the gingival margin with the neck of the tooth or its root exposed: causes and consequences